Page Contents
ToggleIntroduction
Blockchain is a digital ledger of transactions that are managed by a network of computers in a way that is difficult to hack or modify. Technology provides a secure way for individuals to transact directly with each other without the need for an intermediary such as a government, bank, or another third party.
An increasing list of records, called blocks, that are linked together using cryptography. Each transaction is independently verified by a peer-to-peer network of computers, timestamped, and added to a growing data chain. Once saved, the data cannot be changed.


Blockchain was first proposed as a research project in 1991 but it is first widely used in Bitcoin’s transactions Since then, the use of blockchain has exploded with the creation of various cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and smart contracts, real estate purchases, records, and more. healthcare and any other industry that needs to authorize and record a wide range of actions or transactions.
How does blockchain work?
The purpose of blockchain is to record and distribute digital information, but not to edit it. Thus, the blockchain is the basis of an immutable ledger or record of transactions that cannot be altered, deleted, or destroyed. This is why blockchain is known as Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT).
Here we will learn blockchain systems using an example of a bitcoin transaction. First know about the name I,e Blockchain, a chain of blocks. A block in blockchain mainly consists of 3 sections. The first section contains the data about the transaction that is who, what, when, and how much amount of transaction is going to do. The second section contains a Hash. Hash is noting but a fingerprint of the block that is always unique and it is generated through cryptography technique that contains the information of the first section that is the information stored in the first section. A Hash is impossible to read for a human being. The third section contains the Hash of the previous block connected in the chain.
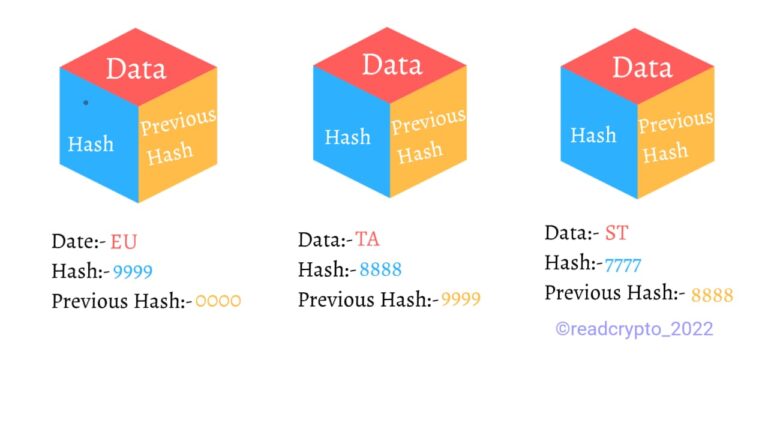

As soon as a purchase or sale is made a block is entered and transmitted to the network of computers known as nodes.
This network of thousands of nodes around the world uses computer algorithms to compete to confirm transactions. This is called Bitcoin mining. The first miners to successfully complete a new block are rewarded in Bitcoin for their work. These rewards are paid in a combination of newly minted bitcoins and network fees and are passed on to buyers and sellers. Fees can be increased or decreased according to transaction volume.
After cryptographic confirmation of the purchase, the sale is added to the block of the distributed ledger. You should then see sales on most networks.
The block is permanently linked to all previous Bitcoin transaction blocks using a cryptographic fingerprint known as a hash and the sale is processed.
Is Blockchain Secure?


Blockchain technology archives decentralized security. If someone is stealing or changing a data of a block that is the changing of the first section of the block happened. As soon as the data is changed the Hash of the block changes. But it is not the New block it is already present in the chain which means the third section of the next block( which contains the Hash of the previous block) will not change making the current block tempered.
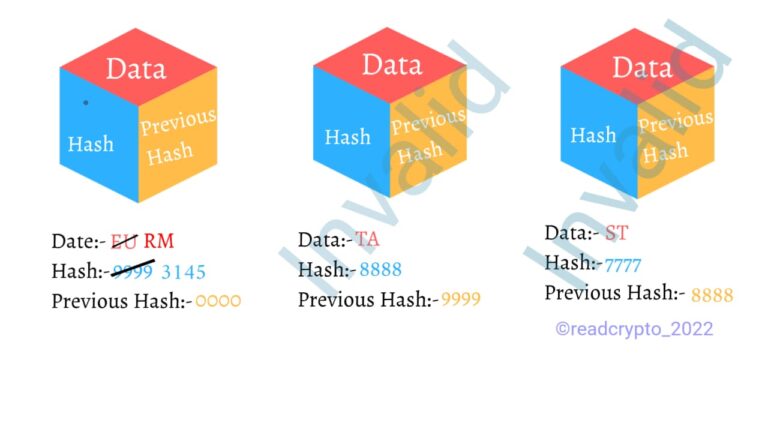

It proves that the changing of the information in any block is insignificant because the majority is in the favour of the correct information. If someone changes the 51% of blocks on the network so that his new copy becomes the majority copy, and thus agreed upon the chain. All though it is next to impossible due to the size of the network of such cryptocurrency.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Cryptocurrency:
Blockchain is also known as Public Ledger Technology. It is decentralized and not controlled by any central authority. As a result of blockchain’s ability to distribute its operations across a network of computers, Bitcoins and other cryptocurrencies do not require a central authority to function. Additionally, this reduces risk and eliminates many of transaction fees. You can read more about it in our cryptocurrency blog.
Healthcare and medicine:
Medical records can be securely stored on blockchain by healthcare providers. Medical records can be generated, signed, and inserted into the blockchain, which provides patients with assurance that the records cannot be altered. Using a private key to encrypt and store these personal health records on the blockchain, they can only be accessed by certain individuals, ensuring their privacy.
Real Estate Record:
You will definitely spend time in Municipal Corporation for processing of property record it is so much time consuming and inefficient
Each error causes tracking property ownership to be less efficient not just because it is time-consuming and costly, but also because it is prone to human error. Documents can be scanned into blockchain and kept in digital form, thus eliminating the need for physical files to be tracked down at local recording offices. Owners can rest assured that their deeds are accurate and permanently recorded if property ownership is stored and verified on the blockchain.
Voting System:
Voting with blockchain will be very significant to eliminate fraud voters. Using blockchain in this way would make tampering with votes nearly impossible. Furthermore, the blockchain protocol maintains transparency in the election process, reducing the number of people needed to conduct an election, and providing officials with near-instant tent A recount would thus not be necessary, and there would be no real concern about fraud threatening this would eliminate the need for recounts or any real concern that fraud might threaten the election.
Smart contracts:
To facilitate, verify, or negotiate a contract, smart contracts can be built into the blockchain. Smart contracts determine the circumstances under which users agree. These conditions must be met in order for the agreement to be carried out.
Pros and cons
Pros:
- Decentralized makes it difficult to alter data
- Security and privacy is maintained
- A way to secure and take full control of their money and documents
- Transparency
Cons:
- Increase in illegal activity because the details of the owners are untrackable.
- Consumes high energy
- Mining fee is sometimes high due to high numbers of transaction
- Blockchain cryptocurrency is highly volatile


Very good post! We will be linking to this great content on our
website. Keep up the great writing.